Process Hazard Analysis: A Complete Guide for PHA
To guarantee safety while lowering dangers Process Hazard Analysis (PHA) is an essential step in numerous industries. Organizations may identify potential risks, analyze risks, and put needed precautions in place to protect staff, the environment, and surrounding areas by using appropriate risk matrix. In this post, we look at various PHA methods and provide useful examples to show how they might be applied in the real world.
TABLE OF CONTENT
- What is Process Hazard Analysis?
- Methods of Process Hazard Evaluation
- Process Hazard Analysis Example
- How to Conduct Process Hazard Evaluation?
- FAQs
1. What is Process Hazard Analysis?
Process Hazard Analysis, also referred to as PHA, is a systematic approach that aims to identify and analyze potential risks related to a process or system. So, it is crucial to manage process safety since it helps companies prevent accidents and improve all other security measures. PHA means an in-depth evaluation of process factors, potential failure systems, and their effects, allowing the development of effective methods for reducing risk.
2. Methods of Process Hazard Analysis
There are several methods that you can use for process hazard analysis. Here are the 5 different methods for risk assessment and process hazard evaluation. Also, you can use risk matrixes for any of them.
-
What if Analysis
What-If Analysis is an interesting approach used in PHA. With the assistance of potential “what if” questions, a group will develop ideas. Organizations can identify process vulnerabilities and try quick solutions by analyzing multiple scenarios that might end up in risk or incidents.
-
Hazard and Operability Study (HAZOP)
Another widely used PHA technique is the Hazard and Operability Study, commonly referred to as HAZOP. This structured approach involves experts meticulously examining each process component, considering parameters, operating conditions, and potential deviations. Through HAZOP, organizations can identify hazards, potential operational issues, and critical vulnerabilities, promoting effective risk management.
-
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
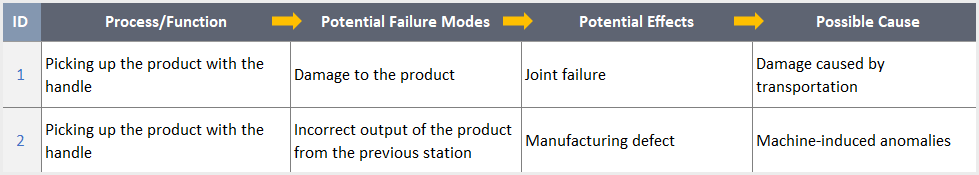
To identify potential failure modes and their impact on the entire system, FMEA entails delving deeply into the detailed intricacies of each process component. The focus of this approach is on examining the likelihood, impact, and severity of failures as well as their effects on people, property, and the environment. In addition, organizations can set priorities for resources and take action by estimating the risks associated with various failure scenarios. You can use FMEA Templates to conduct your failure modes and effects analysis.
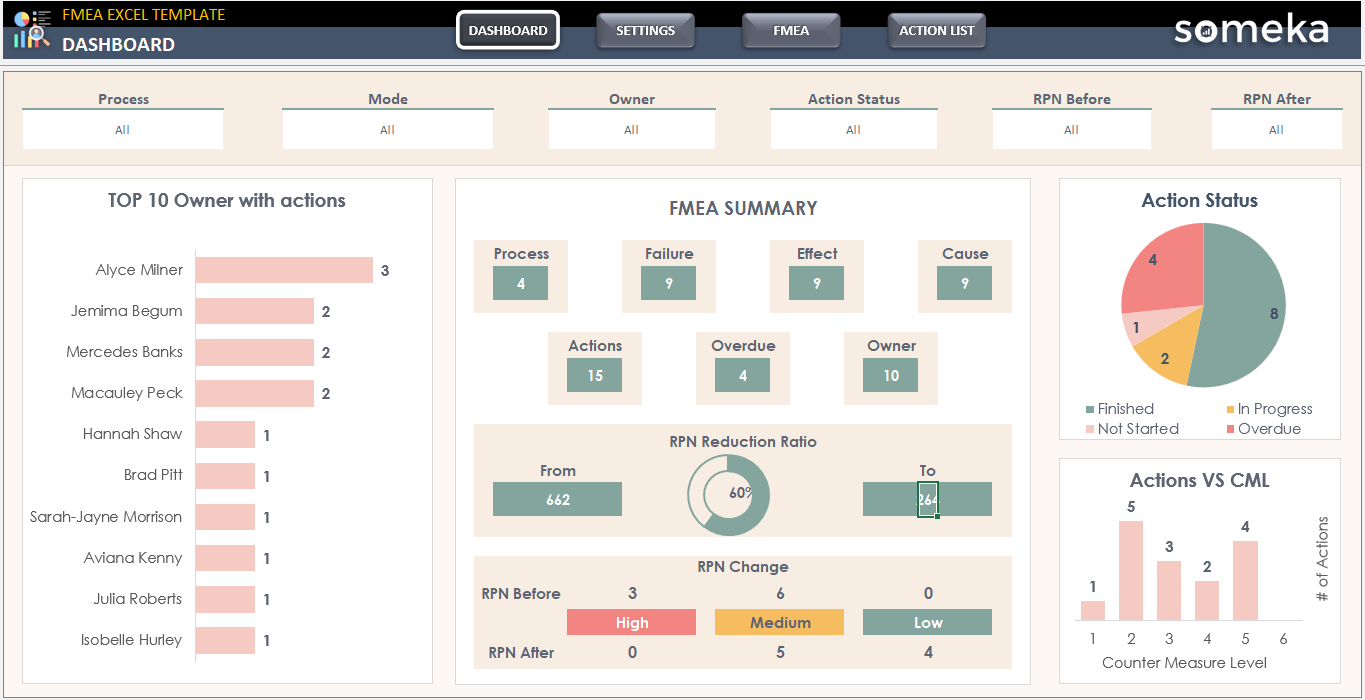
– This Dashboard is from FMEA Excel Template by Someka –
-
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
Think about beginning with an unpleasant event and researching possible reasons or outcomes as you perform an inquiry with FTA. Organizations can see the logical connections between incidents and their causes by creating a fault tree. FTA offers a thorough understanding of how complex systems interact, enabling focused risk-reduction measures.
-
Event Tree Analysis (ETA)
By focusing on the review of impacts following an initiating event, ETA complements FTA. Also, ETA delivers insights into alternate scenarios and their consequences by taking into consideration various possibilities and their probabilities. Organizations can improve making decisions and allocating resources by displaying the order of events and associated probabilities. They can use risk matrixes for event tree analysis.
3. Examples of Process Hazard Analysis
Example: Chemical Production:
For instance PHA discovered a potential risk associated with a particular reaction process in a chemical factory. What-If Analysis discovered that temperature differences beyond a specific limit might set off a runaway reaction, increasing the likelihood of an explosion. Improved temperature control methods and alternative safety systems were successfully put in place to reduce the danger and guarantee employee safety.
Example: Oil Refinery:
For example experts discovered a potential risk related to a crucial pipeline valve problem during a HAZOP examination at an oil refinery. The study raised attention to the danger of a catastrophic release of hazardous materials in the case of valve failure. The refinery minimized the risk and gave staff safety the highest priority by quickly addressing the problem and taking the necessary measures.
4. How to Conduct Process Hazard Analysis?
Do you want to make your industrial operations safer while reducing possible risks? It is crucial to perform an in-depth Process Hazard Analysis (PHA). In this post, we’ll take you step-by-step through the PHA process and offer helpful tips to make sense of this critical component of risk assessment and hazard analysis. Mainly, there are 7 basic steps that you should follow to conduct process hazard protection and risk assessment. Which can be used for risk matrixes.
Step 1 – Establish the Goals and Boundaries:
It’s important to establish the goals and limits of the analysis before digging into PHA. Moreover, to guarantee a targeted and effective PHA, clearly identify the specific procedure or system to be looked over along with boundaries.
Step 2 – Select the Most Effective PHA Techniques:
There are a variety of PHA approaches available; the best one to use depends on the complexity of the process, the level of detail that is wanted, and industry standards. What-If Analysis, Hazard and Operability Study (HAZOP), and Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) are examples of common strategies. Select a methodology that is in line with your objectives and the resources at your disposal.
Step 3 – Collect Useful Data for Process Hazard Analysis:
Furthermore collect all necessary information about the process or system under analysis. This includes process operating procedures, equipment specifications, and any relevant incident or accident reports. Comprehensive information leads to a more effective analysis.
Step 4 – Conduct the Process Hazard Analysis:
Further, it’s time to make the PHA analysis itself. And then the techniques that you choose, systematically evaluate each step and interaction within the process. Identify potential hazards, failure modes, and deviations that may lead to accidents or adverse consequences. You should consider factors such as process conditions, equipment design, and human factors.
Step 5 – Assess Risks and Consequences:
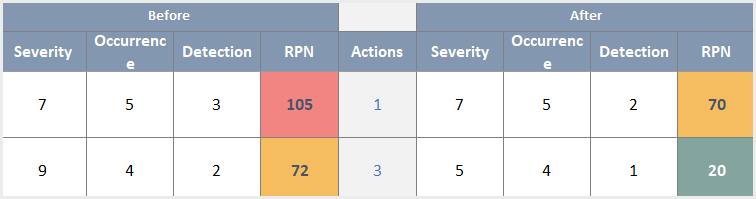
Once hazards are identified, assess the associated risks and potential consequences. Then, evaluate the severity and likelihood of each hazard, taking into account the impact on personnel, the environment, and the surrounding community. You should use the risk matrixes to quantify and prioritize risks, to create efficient risk management strategies.
Step 6 – Create Risk Mitigation Steps:
Moreover based on the identified hazards and their associated risks, you must develop and recommend measurements to reduce risks. This may involve implementing engineering controls, apply procedures, installing safety systems, or providing training programs.
Step 7 – Document All of Your Analysis:
Lastly a report ensures that the findings are communicated to the appropriate parties and serves as a useful resource for future safety assessments. Place a strong understanding on following to OSHA regulations and other legal demands. Also, OSHA regulations are important for dangerous workplaces.
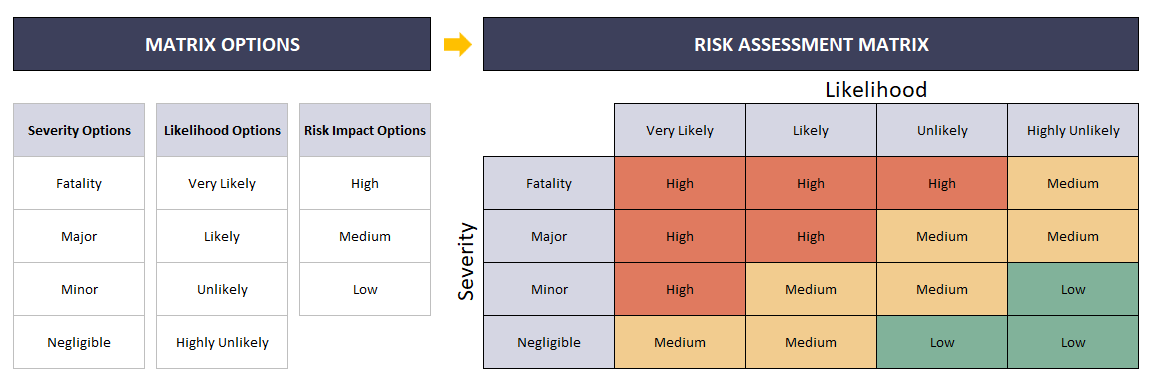
– This dynamic matrix is from Risk Assessment Excel Template by Someka –
5. FAQs
1. What is the difference between PHA and HAZOP?
PHA means process hazard analysis and HAZOP means hazard and operability study. PHA and HAZOP are technics used to assess hazards in production. It focuses on overall risk evaluation, while HAZOP specifically identifies deviations from design or operation. PHA covers various stages, while HAZOP is typically applied during design or modification. PHA considers a wide range of hazards, while HAZOP targets deviations and their consequences. They are both used for OSHA regulations check.
2. What is the difference between FMEA and PHA?
Additionally, FMEA (Failure Modes and Effects Analysis) and PHA (Process Hazard Analysis) are technics used in risk assessment. FMEA specifically analyzes potential failure modes and their effects, while PHA assesses hazards associated with processes. It focuses on failure modes, while PHA covers a broader range of hazards.
3. What are the methods for process hazard analysis?
Likewise, the methods for process hazard analysis include HAZOP (Hazard and Operability Study), What-If Analysis, FMEA (Failure Modes and Effects Analysis), and Fault Tree Analysis (FTA).
4. What are the elements of process hazard analysis?
Lastly, the elements of PHA include hazard problems, risk finding, instant analysis, and the development of risk measurements.
Recommended Readings:
Risk Assessment Process: Importance, Steps, and Framework